Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can cause serious health risks if it accumulates in high concentrations in homes. However, many homeowners are still unaware of these health risks or how to protect themselves and their families. This article will provide you with the information you need to understand the risks of radon in your home and take effective steps to mitigate them.
Radon is an odorless, colorless, and tasteless gas that is produced by the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rocks, and water. As radon is released into the air, it can seep into buildings through cracks in the foundation, walls, floors, and other openings. Once inside, radon can accumulate to dangerous levels, exposing occupants to high levels of ionizing radiation that can damage lung tissue and increase the risk of lung cancer.
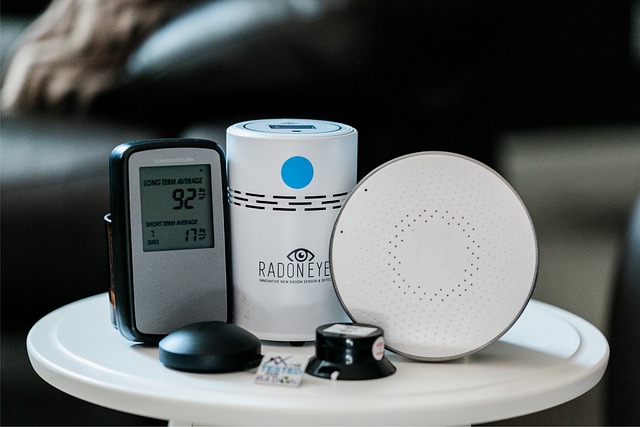

Testing your home for radon. The only way to know if your home has dangerous levels of radon is to conduct a radon test. There are two main types of radon tests: short-term tests that take measurements for two to seven days, and long-term tests that take measurements for more than 90 days. Short-term tests are a good way to get a quick snapshot of radon levels in your home, but long-term tests are more accurate and can provide a better understanding of year-round exposure.
Mitigating radon in your home. If your home has high levels of radon, the good news is that there are several effective ways to mitigate the problem. The most common method is to install a radon mitigation system, which involves sealing cracks in the foundation and installing a vent pipe and fan to draw the radon out of the home and vent it outside. Other methods include increasing ventilation, sealing crawl spaces and sumps, and using radon-resistant construction materials.